general practitioner could rely upon satellites to work in the world, yet its usage precede is a little harder.
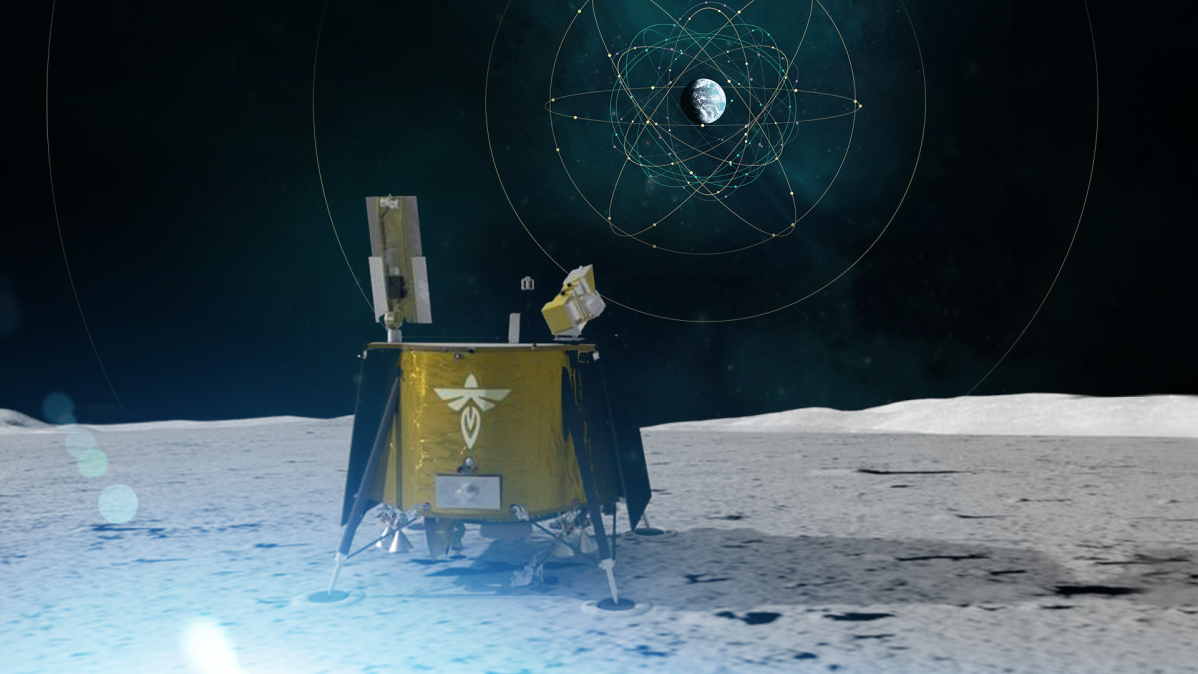
NASA is preparing to check a brand-new lunar navigating system that will certainly link to the Planet’s Worldwide Navigating Satellite System (GNSS) from the moon, a record from the area company discusses.
The unmatched objective will certainly damage a document for the most far-off link to general practitioner at approximately 238,000 miles from Planet’s surface area. It will certainly be supplied to the moon for screening by Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lander no earlier than 2024, NASA claims.
GNSS is composed of satellite constellations that send out placing, timing as well as navigating signals down-to-earth. One of the most typical of all these is GPS, which is run by the U.S. Area Pressure.
Currently, NASA’s Lunar GNSS Receiver Experiment (LuGRE), created as component of a cooperation with the Italian Area Firm (ASI), will certainly compute the very first place repairs from the moon in background.
“LuGRE is the most recent initiative in a lengthy line of goals created to broaden high-altitude GNSS capacities,” stated Fabio Dovis, LuGRE co-principal private investigator at the Italian Area Firm. “We have actually created an advanced experiment that will certainly work as the structure for functional GNSS systems at the Moon.”
LuGRE will certainly link to both general practitioners as well as Europe’s GNSS constellation, Galileo, throughout its journey to the moon. The receiver will certainly additionally perform a variety of navigating experiments while in orbit around the moon prior to getting to the lunar surface area.
Sending out a general practitioner receiver to the moon
As soon as Blue Ghost come down on the moon, the LuGRE receiver will certainly after that release its antenna as well as gather information for approximately 12 days. That information will certainly be returned to Planet, where it will certainly be made use of to aid create lunar GNSS systems for future moon objective, consisting of NASA’s upcoming Artemis III moon touchdown.
“In this instance, we are forging ahead of what GNSS was meant to do — that is, broadening the reach of systems developed to give solutions to earthbound, air travel, as well as maritime customers to additionally consist of the fast-growing area field,” J.J. Miller, replacement supervisor of plan as well as calculated interactions for NASA’s Area Communications as well as Navigating (SCaN) program, clarified. “This will significantly boost the accuracy as well as durability of what was offered throughout the Beauty goals, as well as enable even more adaptable equipage as well as functional situations.”
The LuGRE objective belongs to a larger initiative to boost the performance of GNSS as well as allow its usage at ever-greater elevations. In 2016, NASA’s Magnetospheric Multiscale Goal made use of general practitioners at a record-breaking elevation of 43,500 miles (70,000 kilometres) over the Planet. In 2019, on the other hand, MMS damaged its very own document by repairing its place with general practitioner at an elevation of 116,300 miles, nearly halfway to the moon. With LuGRE, NASA will certainly greater than dual that range when it releases its brand-new system from the lunar surface area.